What is Graphical User Interface GUI Detail Answer
Graphical User Interface provides the user graphical means to interact with the system. GUI can be combination of both hardware and software. Using GUI, user interprets the software.
Typically, GUI is more resource consuming than that of CLI. With advancing technology, the programmers and designers create complex GUI designs that work with more efficiency, accuracy and speed.
GUI Elements
GUI provides a set of components to interact with software or hardware.
Every graphical component provides a way to work with the system. A GUI system has following elements such as:
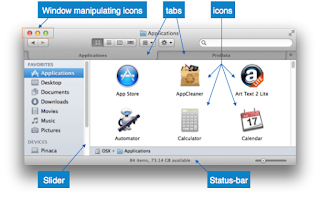
· Window - An area where contents of application are displayed. Contents in a window can be displayed in the form of icons or lists, if the window represents file structure. It is easier for a user to navigate in the file system in an exploring window. Windows can be minimized, resized or maximized to the size of screen. They can be moved anywhere on the screen. A window may contain another window of the same application, called child window.
· Tabs - If an application allows executing multiple instances of itself, they appear on the screen as separate windows. Tabbed Document Interface has come up to open multiple documents in the same window. This interface also helps in viewing preference panel in application. All modern web-browsers use this feature.
· Menu - Menu is an array of standard commands, grouped together and placed at a visible place (usually top) inside the application window. The menu can be programmed to appear or hide on mouse clicks.
· Icon - An icon is small picture representing an associated application. When these icons are clicked or double clicked, the application window is opened. Icon displays application and programs installed on a system in the form of small pictures.
· Cursor - Interacting devices such as mouse, touch pad, digital pen are represented in GUI as cursors. On screen cursor follows the instructions from hardware in almost real-time. Cursors are also named pointers in GUI systems. They are used to select menus, windows and other application features.
Application specific GUI components
A GUI of an application contains one or more of the listed GUI elements:
· Application Window - Most application windows uses the constructs supplied by operating systems but many use their own customer created windows to contain the contents of application.
· Dialogue Box - It is a child window that contains message for the user and request for some action to be taken. For Example: Application generate a dialogue to get confirmation from user to delete a file.
· Text-Box - Provides an area for user to type and enter text-based data.
· Buttons - They imitate real life buttons and are used to submit inputs to the software.
· Radio-button - Displays available options for selection. Only one can be selected among all offered.
· Check-box - Functions similar to list-box. When an option is selected, the box is marked as checked. Multiple options represented by check boxes can be selected.
· List-box - Provides list of available items for selection. More than one item can be selected.
Other impressive GUI components are:
- Sliders
- Combo-box
- Data-grid
- Drop-down list
User Interface Design Activities
There are a number of activities performed for designing user interface. The process of GUI design and implementation is alike SDLC. Any model can be used for GUI implementation among Waterfall, Iterative or Spiral Model.
A model used for GUI design and development should fulfill these GUI specific steps.
· GUI Requirement Gathering - The designers may like to have list of all functional and non-functional requirements of GUI. This can be taken from user and their existing software solution.
· User Analysis - The designer studies who is going to use the software GUI. The target audience matters as the design details change according to the knowledge and competency level of the user. If user is technical savvy, advanced and complex GUI can be incorporated. For a novice user, more information is included on how-to of software.
· Task Analysis - Designers have to analyze what task is to be done by the software solution. Here in GUI, it does not matter how it will be done. Tasks can be represented in hierarchical manner taking one major task and dividing it further into smaller sub-tasks. Tasks provide goals for GUI presentation. Flow of information among sub-tasks determines the flow of GUI contents in the software.
· GUI Design & implementation - Designers after having information about requirements, tasks and user environment, design the GUI and implements into code and embed the GUI with working or dummy software in the background. It is then self-tested by the developers.
· Testing - GUI testing can be done in various ways. Organization can have in-house inspection, direct involvement of users and release of beta version are few of them. Testing may include usability, compatibility, user acceptance etc.


No comments:
Post a Comment